What is In Vitro Fertilization?
What is IVF?
In vitro fertilization (IVF) is a method of assisted reproduction in which a man's sperm and a woman's eggs are combined outside of the body in a laboratory dish. One or more fertilized eggs (embryos) may be transferred to the woman's uterus, where they may implant in the uterine lining and develop. Excess embryos may be cryopreserved (frozen) for future use. Initially, IVF was used to treat women with blocked, damaged, or absent fallopian tubes. Today, IVF is used to treat many causes of infertility, such as endometriosis and male factor, or when a couple's infertility is unexplained.
When is IVF indicated for an infertile couple?
IVF was initially used to treat women with blocked, damaged, or absent fallopian tubes. Today, IVF is used to treat many causes of infertility, such as endometriosis and male factor, when a couple's infertility is unexplained or in women with advanced maternal age where her chances for pregnancy are rapidly declining and IVF remains as the best possible option.
What are the steps in the IVF process?
The basic steps in an IVF treatment cycle are ovarian stimulation, egg retrieval, fertilization embryo culture, and embryo transfer. During ovarian stimulation, medications or "fertility drugs," are used to stimulate multiple eggs to grow in the ovaries rather than the single egg that normally develops each month. Using ultrasound examinations and blood testing, the physician can determine when the follicles are appropriate for egg retrieval (Figure 1). Generally, eight to 14 days is required. When the follicles are ready, hCG or other medications are given.
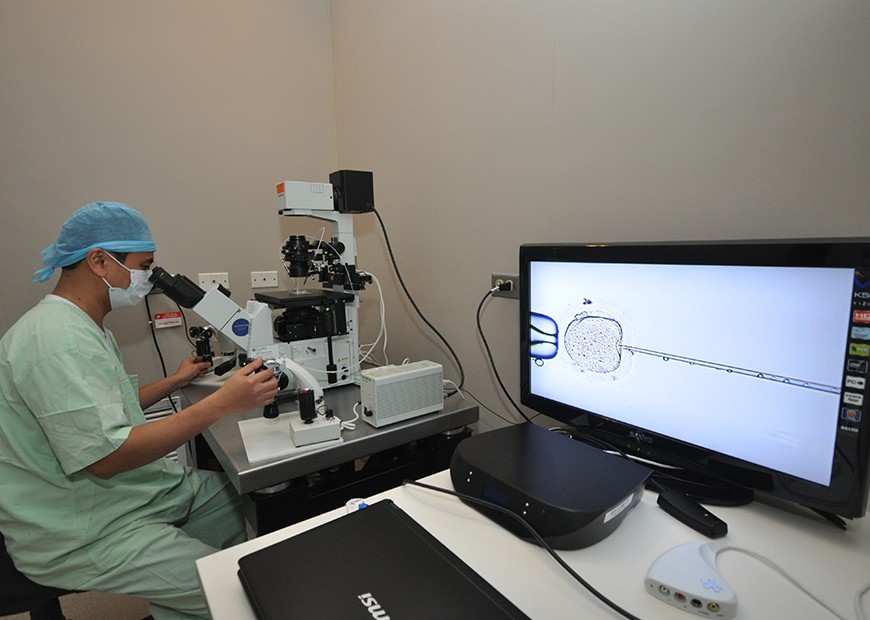
Egg retrieval is done before ovulation occurs, usually 34 to 36 hours after the hCG injection. It is usually accomplished by transvaginal ultrasound aspiration, a minor surgical outpatient procedure (Figure 2) that is done with some form of analgesia administered. The eggs are aspirated from the follicles through the needle connected to a suction device with the guidance of ultrasound probe inserted through the vagina. Removal of multiple eggs can usually be completed in less than 30 minutes. In some circumstances, one or both ovaries may not be accessible by transvaginal ultrasound and laparoscopymay then be used to retrieve the eggs using a small telescope placed in the umbilicus. In the phase of fertilization and embryo culture,the retrieved eggs are examined in the laboratory for maturity and quality (Figure 3). Mature eggs are fertilized by micro-insemination or intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI). The next day, the eggs are evaluated for signs of fertilization and are kept under special conditions to allow further growth and development. Depending on the program, developing embryos may be cultured in the IVF lab for two to six days after the egg retrieval and become.embryos from 2-cells to blastocysts (Figure 4).
During embryo transfer, the physician and the embryologist inform the couple about the quality and number of available embryos and discuss the options before the couple decides on the number of embryos for transfer. Once a decision is made, the embryologist loads the embryo/s into a transfer catheter while the physician prepares the patient. No anesthesia is necessary, although some women may wish to have a mild sedative. Once the catheter is prepared, it is quickly handed over to the physician who gently guides the tip of the transfer catheter through the cervix and places the fluid containing the embryos into the uterine cavity (Figure 5). The patient is then given additional medications for 2 weeks after which a serum pregnancy test is done.
How long is the IVF process?
The average time that is required to complete one IVF cycle (from start of ovarian stimulation to testing for pregnancy) is about four to six weeks, depending on the chosen ovarian stimulation protocol appropriate for your case.
What is ICSI?
Intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) is the step in the IVF process which aims to achieve fertilization for the collected eggs. In ICSI, a single sperm is directly injected into each mature egg (Figure 6). ICSI is usually performed when there is a likelihood of reduced fertilization, i.e., poor semen quality, history of failed fertilization in a prior IVF cycle, etc.
What are my chances to achieve success in an IVF cycle?
Your chances will depend on a few factors, most crucial of which are women’s age, presence of co-morbidities (endometriosis, previous ovarian surgery), and quality of husband’s sperm). In addition, success rates vary from center to center and between practicing clinicians. Generally, pregnancy rates from a single IVF cycle may range from 20% to 80% depending on the clinical picture per case. Do ask your doctor regarding your chances after full evaluation.
How do I increase my chances in IVF?
Patients themselves may help increase their chances by approaching their ideal body weight and by avoiding avoiding certain lifestyle habits (smoking, alcohol-drinking, caffeine-drinking). Studies have shown that women who are within normal body mass index (BMI) 20-24 kg/m2 tend to have a higher chance of success during IVF than women who have higher or lower BMI values. Similarly, some reports have shown that cigarette-smoking and alcohol-drinking, by either the wife or the husband especially during the time of IVF treatment significantly decreases their chances of a successful outcome. A similar recommendation regarding coffee-drinking has also been reported. For these reasons, these lifestyle habits must be avoided during an IVF try.